
In the late 1930s, the search for versatile monomers led chemists toward the acrylates. By the post-war era, 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate found favor in Europe and North America. Factories chased new plastics and paints to turbocharge growth, pumping out batches as economies shifted from coal and steel to chemicals and consumer goods. Many old-timers in the field will recall the pages of their college organic chemistry texts, littered with discussions about late-stage acrylate esters and how they fed the adhesive revolutions in the 60s. When Eastern European manufacturers started setting up continuous reactors in the 1980s, markets picked up speed—and regulation followed. Modern producers now face relentless pressure to innovate without triggering headlines about worker exposure or environmental spills.
2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate belongs to the class of monomeric acrylates known for flexibility and tackiness. Folks think of it as an ingredient for products needing a soft, flexible touch, like pressure-sensitive adhesives, sealants, and coatings. It’s also not a stranger to textiles and plastics. The easy flow and compatibility with other acrylic monomers make it a go-to option in many polymerization recipes. Some call it the “plasticizer’s friend,” since it helps finished products resist cracking and weathering under season after season of use.
A bottle of 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate smells faintly sweet, a clear liquid, almost oily, with a density just under 0.89 g/cm³ and a boiling point rounding 215°C. It’s not going to freeze easily in the winter—its freezing point sits well below common storage temperatures. The refractive index sits at about 1.439. One thing you notice after working with it long enough: it’s light, volatile, and will eat through poor-quality gloves. The solubility in water is low but dissolves easily in organic solvents like acetone or alcohols. Its double bond calls for attention, making it a reactive starting point for both addition and copolymerization reactions.
Industrial grades usually demand a minimum purity around 99.0%, with acidity as acetic acid held below 0.01%. Peroxides and inhibitors, typically hydroquinone or MEHQ, keep the product from polymerizing in the tanker truck before delivery. Producers mark drums with UN1993 or the proper shipping name under DOT regulations and refer to GHS pictograms for flammability and health hazards. Every shipment comes anchored by a robust certificate of analysis. In my experience, inspectors raise eyebrows at cloudy samples or missing inhibitor labels—there’s history behind every careful word on a safety datasheet.
Most 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate comes from the reaction of acrylic acid with 2-ethylhexanol. Factories rely on acid-catalyzed esterification, driving off water under reflux. Trained operators watch for the right temperature and pressure to avoid runaway reactions. Downstream, distillation removes residual acid and excess alcohol to boost purity. Some plants recapture solvents and monomers for the next batch, applying lessons from green chemistry to cut costs and lower emissions. It reminds me of long nights troubleshooting pilot-scale runs, where a stuck distillation column could bring the line to a halt.
The acrylate group loves to take part in free-radical polymerizations. Copolymerization with methyl methacrylate or vinyl acetate lets you dial in adhesive strength or water resistance. Labs sometimes modify it further by introducing functional side groups to tailor the polymers for medical patches or advanced coatings. Researchers mix in UV-initiated systems—or introduce block copolymers with smart mechanical properties. A batch gone awry shows how sensitive process controls need to be, since runaway reactions aren’t just theoretical—they occasionally burn out pumps and eat up profit margins.
In the trade, you might hear it called 2-EHA, octyl acrylate, or its full tongue-twisting title: 2-ethylhexyl prop-2-enoate. Some brands stick with industrial-sounding SKUs like “Acrylate O 312,” while others push lighter names for glossy brochures. Regardless, a check of the CAS registry number (103-11-7) sets the record straight. It’s smarter to check labels twice before mixing, since containers sometimes share warehouses with other acrylates—and confusion can cost money and safety.
Workplaces storing or using 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate rely on solid ventilation. Mask up, glove up—this stuff irritates skin and lungs. Spills lead to slippery floors and a flammable vapor cloud waiting for a static spark. While most agencies, from OSHA to ECHA, assign it moderate concern in toxicological terms, older studies caution about sensitization. So companies train workers, invest in spill response, and keep drums under nitrogen blankets. Over the years, stories emerge about workers who ignored safety goggles—ending up with painful chemical burns. Regulations didn’t appear out of thin air; they followed real-world accidents.
Adhesive factories run on this stuff, especially for tapes and labels that stick fast but peel away cleanly. You find it in sealants for construction joints, automotive weather-stripping, and flexible plastics. The paint and coatings industry values its ability to stretch film and resist the cracking that sunlight brings. Disposable hygiene products, medical patches, and even waterproofing membranes use 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate for its staying power and safety profile. Nobody wants a sticker that falls off or a sealant turning brittle in one summer.
Research teams keep playing with copolymerization options, targeting greener, safer, and more durable polymers. The push for lower-VOC paints brought a wave of acrylic research using 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate as a backbone. Studies from top universities look at bio-based alternatives to nudge the industry away from petrochemicals. Labs chase after formulations that resist UV, adapt properties at the nanoscale, or use less energy during production. As regulatory heat rises, innovation doesn’t slow. Anyone following the literature sees fresh patents filed each year—new processes or tweaks to old ones, each promising fatter margins or smaller carbon footprints.
Despite decades of data, toxicologists don’t stop investigating. Acute studies point to mild-to-moderate irritation upon skin or eye contact, calling for careful PPE. Respiratory effects tend to show up with high vapor concentrations—something nontrivial in confined spaces. Chronic exposure data remains limited, but most animal models suggest low carcinogenicity. That reassures some but calls for more data, especially with rising pressures from NGOs. In one industry-wide review, researchers found no definitive links between long-term occupational exposure and increased cancer risk, though skin sensitization stays on watchlists. The safest bet? Apply the controls and respect the warnings—nobody wants to end up in the next health advisory.
The road ahead looks busy for 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate. Sustainability efforts demand reactants with smaller environmental footprints. Researchers toy with recyclable and compostable acrylates, tinkering with production streams to save energy or trade fossil feedstocks for renewable ones. Industry customers press for lower emission adhesives and coatings. Regulation shapes the pace, but application engineers always push for stronger, lighter, and safer compounds. With consumer demand flexing under economic and environmental pressures, those working with this monomer will keep adapting, learning from the past to guide better choices in the lab and on the shop floor.
You’ll find 2-ethylhexyl acrylate in plenty of products around your home, office, and car. This chemical helps make things stick, flow, and flex—qualities that sound simple but make a big difference in the things we touch every day. Think about the clear tape holding up a note on the fridge or that fresh coat of acrylic paint brightening up a wall. Without this compound, both would look and feel pretty different—or in some cases, wouldn’t work at all.
From masking tape to those heavy-duty industrial labels, adhesives need a polymer base that can stretch and stick without becoming brittle. 2-ethylhexyl acrylate supplies that elasticity. Over the years, researchers discovered that adding this ingredient makes glue smoother and less likely to crack or peel. The slippery quality of the molecule lets adhesives grip surfaces without leaving behind a mess. That’s something I’ve noticed on dusty construction sites where regular tapes dry out and fall off, while the better ones hold on through all kinds of weather.
People expect paint to stick to walls, dry evenly, and resist peeling for years. Paint manufacturers use 2-ethylhexyl acrylate to keep their coatings flexible and glossy. Without it, you’d see more flaky walls and dull finishes. It acts like a plasticizer—a sort of softening agent—so the paint doesn’t become as hard or crack over time. This all comes down to the way the molecule moves among the paint’s other ingredients, making sure everything sets up right. Whether painting a house, a fence post, or even street markings, consistency and flexibility matter much more than folks think.
Protecting surfaces—bridges, car parts, medical devices—means using materials that last, even under tough conditions. 2-ethylhexyl acrylate pops up in these coatings too. It helps create films that block out moisture and handle expansion and contraction without breaking up. In the medical world, think of the flexible patches on a patient’s skin or the strong adhesive on a bandage; it’s inside many of those products for the same reasons. Hospitals depend on reliable stickiness and safety, so ingredient quality gets strict checks. Studies highlight low toxicity at common exposure levels, making it a trusted part of medical adhesives and dressings.
Factories making or using 2-ethylhexyl acrylate need solid protections for workers. This chemical can irritate the skin or eyes, and breathing it in vapor form causes problems after long exposure. Regular monitoring, good ventilation, and proper gloves don’t feel negotiable. Adding more education about chemical risks and investing in personal protective gear builds trust and keeps people safe.
Some scientists push to find alternatives with lower environmental footprints. The waste from acrylate production raises concerns, especially for waterways. Research digs into plant-based versions or recycling streams that cut pollution. It’s a challenge to balance performance and safety, but new ideas keep popping up in university and commercial labs. The goal? Strong, flexible materials that protect both people and the planet.
Every time I pull a sticker off its backing or peel away a label without leaving behind a sticky mess, I have 2-ethylhexyl acrylate partly to thank. This colorless liquid might not be something most people have heard of, but it quietly shapes products we use every single day. Its real value comes from how it lets manufacturers create flexible, durable plastics and adhesives that handle stress and weather without cracking or falling apart.
2-Ethylhexyl acrylate stands out because it brings a soft, plastic-like flexibility to the materials it joins. Add it to a polymer, and its long, branched carbon chain pushes the polymer chains apart, keeping them from sticking too closely together. This stops the finished product from becoming hard or brittle—a property prized by anyone who has watched clear packing tape shatter in the cold.
Its low glass transition temperature plays a big part here. Most people don’t think in terms like "glass transition temperature," but it marks the point where a substance moves from being glassy and fragile to soft and rubbery. For 2-ethylhexyl acrylate, this temperature sits far below freezing, so its presence keeps glues, coatings, and films pliable even in harsh winter weather.
Another feature that sets this liquid apart: chemical resistance. Home improvement projects and automotive repairs often demand materials that shrug off water, sunlight, and many household chemicals. Products containing this acrylate hold up through spills and UV exposure better than many alternatives, leading to fewer replacements and less frustration for folks who don’t want to do the same job twice.
Unlike short-chain acrylates, which can bring a harsh odor and stiff performance, the longer carbon chain in 2-ethylhexyl acrylate knocks down the smell and introduces extra flexibility. I’ve worked with adhesives that rely on this compound for exactly this reason; you’re spared the migraine so common with more volatile plasticizers.
Safety always sits near the front of my mind, especially after seeing plenty of industrial accidents reported over the years. 2-Ethylhexyl acrylate can irritate skin and eyes if handled carelessly. Lab workers and factory staff wear gloves and goggles, and guidance from the European Chemicals Agency calls for proper ventilation to limit risk. So while it’s not classified as a major health hazard, basic respect for chemical safety pays off.
On the environmental front, concerns focus on leaks into soil or water. This acrylate doesn’t break down overnight, and studies show that if spilled, it can persist, potentially harming aquatic life. Industry groups and environmental watchdogs push for proper containment and disposal to keep damage in check. Challenge emerges, though, in tracking smaller-scale uses outside big factories, which may slip through regulatory nets.
Scientists continue to search for alternatives with even safer profiles, but so far, 2-ethylhexyl acrylate remains one of the best choices for durability and flexibility in many products. Strengthening rules around storage and emissions could lower accident rates and environmental impact. It’s a case where prioritizing local oversight and worker training makes a real difference, since the properties that make this chemical great for products also mean it lingers if mishandled.
In short, the next time I marvel at a weather-resistant label or unstressed stretch film, I’ll be thinking of this humble acrylate once again—shaping modern life in ways that most folks never even see.
Walk into most hardware stores or job sites, and you’ll find caulk, paint, and adhesives—a lot of them list their ingredients in tiny print on the label. One chemical, 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate, keeps showing up. From my own experience working around construction and renovation, curiosity is natural: Does this stuff pose a danger? Is it toxic if you touch or breathe it?
2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate forms the backbone of many plastics and rubbers. You won’t find it sitting on a shelf by itself, but it works as a building block in products people use every day, including weatherproof adhesives and glossy coatings on cars. Most folks never handle the pure substance—chemical workers, lab techs, and some factory employees are the ones most likely to come into close contact.
Studies out of regulatory agencies like the EPA and the European Chemicals Agency spell out what can go wrong. Breathing in the vapor, especially in closed, badly ventilated areas, irritates lungs and eyes. In some cases, even short-term exposure brings on headaches, watery eyes, or sore throats. I’ve seen guys get red hands or little blisters after barely touching the uncured goop. Over longer stretches, folks working with high concentration run risk of getting their skin sensitized. That means even a small brush with it later triggers rashes or itching.
The science shows plenty of warning signs. Animal studies back up what workers have noticed: repeated exposure brings on chronic allergic reactions or inflamed skin. There’s also growing concern about what happens if this chemical gets into the environment. Spills into waterways threaten fish and tiny aquatic creatures, which sets off alarms higher up the food chain. Drinking water tests haven’t flagged a widespread hazard for the general public. Even so, factories and workplaces with poor controls put their people at more risk—not just from sudden spills, but through slow, repeated exposure.
Regulators in Europe and North America classify 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate as a possible skin sensitizer. OSHA and similar groups force employers to post warnings, offer gloves and masks, and install proper ventilation. Over the years, I’ve noticed many small companies skimp on personal protection, especially during summer when people get lax about gloves and face shields. This chemical doesn’t smell all that strong or unpleasant, so folks drop their guard.
Manufacturers and users need to lean into transparency. It helps when container labels speak plainly, warning about real world symptoms, not just vague risks. Regular air-quality testing makes a long-term difference in factories, as does rotating workers so one operator doesn’t get hit day after day with the same fumes. Training teams to recognize the signs of irritation or allergy pays off—it lets people catch problems early, reducing missed work and health problems.
Home renovators and DIY folks should never assume that “hardware store safe” equals zero hazard. Read the label. Wear basic nitrile gloves, keep a window open or a fan running, and don’t rush clean-up. It’s a practical approach that fits with how most people get projects done, whether on a job site or fixing up a bathroom at home.
I’ve seen the stories and the data line up: most injuries come from routine, not from freak accidents. Take the hazard seriously, make safety a habit, and there’s little to fear from using products containing 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate. If you work in a setting that uses lots of adhesives, demand clear rules and follow through each time you suit up. Health isn’t worth cutting corners, especially not for something that may cause long-term trouble down the road.
Working with chemicals like 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate brings many safety concerns front and center. This liquid, widely used in adhesives and paints, carries significant hazards. Contact can irritate the skin and eyes, and inhaling its vapors may trigger headaches, dizziness, or worse. I have learned, through years around industrial materials, that taking the risks seriously from the start helps avoid costly accidents later.
This compound reacts quickly with heat, light, and air. Left out in the open or stored in a hot spot, it degrades. Polymeric sludge can form, which not only ruins the chemical but also blocks pipes and damages equipment. A cool, dry space is essential. Store the containers in a well-ventilated place away from direct sunlight, ignition sources, and incompatible substances like strong acids or bases. Flammable liquid storage cabinets provide an extra layer of protection. Routine checks on the condition of storage drums—looking especially for leaks or signs of corrosion—save headaches down the road. Locked storage with clear labeling keeps unauthorized or untrained folks from dangerous mistakes.
Handling begins with the right gear. Nitrile gloves, chemical splash goggles, and protective clothing block direct contact. In closed spaces, I have found that organic vapor respirators or fitted masks matter more than you might think. Even a small whiff can linger in your nose for ages. Pouring or transferring the chemical should always happen over spill containment trays. A simple drip can spread, causing slippery floors and chemical burns on contact.
Pumps and transfer tools, if properly grounded, help guard against static discharge and accidental fire. In shops that use 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate daily, grounding practices become muscle memory. Training everyone who works in the vicinity about hazards, first aid, and emergency procedures cannot be skipped. I have seen confusion during incidents slow down the response—clear guidance and regular drills help teams act fast.
Spills demand immediate cleanup, but rushing in without preparation makes things worse. Absorbents for organic chemicals keep liquid from spreading. Mixing the spill into regular workplace trash can create dangerous reactions, so keeping a dedicated chemical waste container nearby is a must. Contacting a certified hazardous waste company for disposal keeps both workers and the environment safe. At one site, waiting too long to address a leaking drum resulted in months of smell and soil cleanup; having a plan in place avoids that kind of headache.
The long-term health risks of repeated low-level exposure stack up quickly—chronic respiratory issues, skin sensitivity, even higher risks of chemical allergies. The U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) both identify strict safe handling measures for good reason. Following rules protects workers, communities, and anyone downstream of waste or runoff.
Continuous improvement stands out. Upgrading to sturdier storage containers, installing better ventilation, investing in spill response kits, and reinforcing training all reduce risk. Digital tracking of stock and expiration dates keeps old product from breaking down unnoticed. Listening to workers brings new insights—often, those on the floor spot early warning signs first.
Safe handling and storage protect people, property, and the broader environment. Complacency leads to damage, illness, and financial loss. A careful approach, drawing on facts and daily experience, keeps danger at bay and business moving forward.
Most casual shoppers won’t recognize the name 2-ethylhexyl acrylate, but if you’ve ever bought a bandage, peeled a sticky label, or watched a deck withstand a sudden rainstorm, you’ve crossed paths with it. This compound might lack flashiness, but its workhorse role in industry deserves more credit than it gets. It acts as a building block for soft, durable plastics and is particularly valued in acrylic-based products.
Think about stickers, tape, or even graphics on packaging—you probably interacted with pressure-sensitive adhesives today. 2-ethylhexyl acrylate adds a stretchiness and flexibility that keeps tape and self-adhesive labels sticking but also lets you peel them off without tearing everything apart. My own experience with kids’ school projects comes to mind. Cheap stickers without this acrylate tend to rip or leave a stubborn mess, while the good quality ones come off cleanly, sparing the kitchen table.
Outdoor paint often faces heat, rain, snow, and everything in between. Manufacturers use 2-ethylhexyl acrylate in emulsion paints to toughen coatings yet keep them flexible enough to resist cracking and peeling. I noticed on my backyard fence: cheaper paint started flaking after a couple of winters, but formulations based on acrylic polymers with 2-ethylhexyl acrylate stayed intact through freeze-thaw cycles. The same chemical offers dirt and water repellent properties in architectural and automotive coatings, helping surfaces handle regular cleaning.
Coated fabrics in upholstery, car interiors, and rain gear owe some of their comfort to acrylate-based formulations. The soft stretchiness from this compound means seat covers, mats, or rainjackets don’t become brittle or stiff with age or exposure. Textile finishing processes use it to form a durable, washable film that feels pleasant and adapts to movement. I’ve had the same waterproof jacket for years—even after many washes, it hasn’t gone stiff or lost its protective quality, because of these resilient coatings.
On the building site, sealants and caulks need toughness with a forgiving, rubbery feel. Expansion joints and window frames, for example, move as temperatures change and buildings settle. Acrylate copolymers—including those built with 2-ethylhexyl acrylate—prevent cracking and leaks by flexing instead of failing. The home handyman in me appreciates not having to redo leaky windows after just a season, since products that flex with building movement have a longer lifespan.
Chemicals like 2-ethylhexyl acrylate need careful handling. Studies show skin or eye contact can cause irritation, so good ventilation and protective gear are vital for workers. Handling guidelines exist for production and installation to keep exposures low. As for environmental footprint, wastewater treatment captures much of the residue at factories, yet ongoing research and stricter regulations around disposal, especially in Europe and North America, reflect industry attempts to minimize pollution.
Green chemistry efforts offer promise: researchers are chasing plant-based feedstocks and safer formulations. That said, stepping away from fossil-sourced chemicals is a tall task, both economically and technically. Companies experimenting with bio-based acrylates hope to keep flexibility and durability at the same levels, all while reducing their ecological impact. Until then, 2-ethylhexyl acrylate keeps daily life a bit more comfortable, clean, and reliable—quietly doing its job behind the scenes.
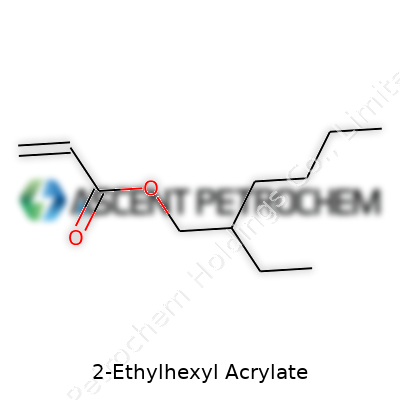
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | 2-ethylhexyl prop-2-enoate |
| Other names |
Acrylic acid 2-ethylhexyl ester 2-Ethylhexyl ester of acrylic acid 2-EHA Acrylsäure-2-ethylhexylester |
| Pronunciation | /tuː ˈɛθ.ɪlˌhɛk.sɪl əˈkraɪ.leɪt/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 103-11-7 |
| Beilstein Reference | '1858733' |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:31589 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL148769 |
| ChemSpider | 8017 |
| DrugBank | DB14172 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.091.276 |
| EC Number | 203-080-7 |
| Gmelin Reference | 93097 |
| KEGG | C21142 |
| MeSH | D017350 |
| PubChem CID | 31232 |
| RTECS number | RG3840000 |
| UNII | K50W4WZG1L |
| UN number | UN 2283 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | CXT1-AP25Q1 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C11H20O2 |
| Molar mass | 130.18 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Odor | Characteristic |
| Density | 0.885 g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble |
| log P | 4.09 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.1 mmHg (20 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 13.7 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 11.57 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -7.81×10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.434 |
| Viscosity | Viscosity: 1.1 mPa·s (20 °C) |
| Dipole moment | 1.66 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 489.6 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -471.7 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -4234 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS02,GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H315: Causes skin irritation. H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction. H319: Causes serious eye irritation. H332: Harmful if inhaled. |
| Precautionary statements | Precautionary statements for 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate as a string: "P210, P261, P273, P280, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P333+P313, P337+P313, P362+P364, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 2-2-2-0 |
| Flash point | > 79 °C |
| Autoignition temperature | 220°C (428°F) |
| Explosive limits | Explosive limits: 0.9–8.1% |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 (oral, rat) 5,000 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): Oral, rat: 5,000 mg/kg |
| NIOSH | RX8225000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | PEL: 10 ppm (TWA) |
| REL (Recommended) | 5 mg/m3 |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | IDLH: 250 ppm |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
Acrylate Methyl acrylate Butyl acrylate Ethyl acrylate Methacrylate 2-Ethylhexanol |